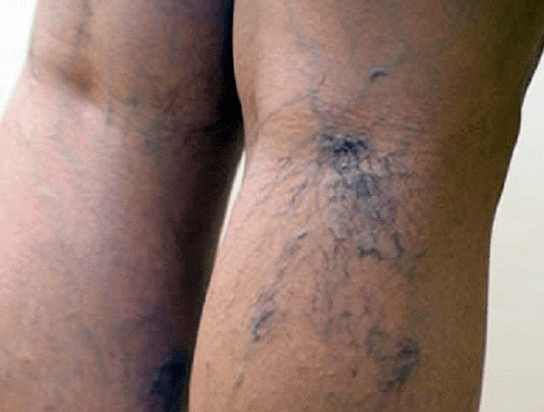
Varicose veins in the legs are characterized by the formation of saccular dilatations of the superficial (subcutaneous) veins of the lower extremities, their serpentine tortuosity, an increase in length due to a violation of the outflow of blood through them and congestive changes in the lower extremities.
The term "varicose disease" comes from the Latin word varix, which means "tortuous, intertwined. "
Mankind has been familiar with varicose veins since ancient times. When conducting archaeological research during the excavations of the Mastaba burial in Egypt from 1595-1580. BC. a mummy was found with signs of varicose veins and treatment of a venous trophic ulcer of the leg.
This disease is considered to be humanity's payment for the possibility of upright walking. Varicose veins in the legs affect an average of about 15% of men and up to 25% of women (including pregnant women) in economically developed countries. The high-risk group includes women, overweight people, people with a profession associated with a long load on the lower limbs, who have to stand or sit for a long time at work.
Classification
Taking into account the factors predisposing to the development of the disease, primary and secondary varicose veins in the legs are distinguished for various reasons.
- Primarydevelops with varicose veins. With varicose veins, the superficial veins change first of all, while the deep veins have a normal structure and function. For a long time, varicose veins appear only as a cosmetic defect, but later, as the disease progresses, venous outflow disturbances occur, as a result of which pain in the lower extremities, swelling of the feet and legs, darkening of the skin in the lower third of the leg, inflammatory changes and trophic changes begin to appear. ulcers. Varicose veins are a continuously progressive disease.
- Secondaryis a complication of deep vein disease, in particular, it develops either as a result of congenital malformations of the venous system (fistulas, congenital dysplasia, etc. ), or after phlebothrombosis. Phlebothrombosis is a complex process of thrombus formation in the deep main veins of the lower extremities, as a result of which blood flow through the deep veins is disturbed. Over time, the forming thrombus is fixed in the vein, holes appear in it through which a limited blood flow is possible, however, the venous valves at the location of the thrombus are scarred and cease to prevent the reverse flow of blood. As a result of dysfunction of the valves of the deep veins, the blood begins to move up and down through them, flows back into the superficial veins and develops secondary varicose veins. As a result, favorable conditions are created for venous stasis, especially in the lowest parts of the limb - the foot and lower leg.
Symptoms of varicose veins
In most people, varicose veins appear as a cosmetic defect, most commonly found on the inner surface of the lower legs. Sometimes varicose veins can manifest only as a venous cobweb, which is formed when veins of small diameter change, most often on the legs and less often on the face or upper limbs. Varicose veins acquire a blue or dark purple color, tortuous course.
Symptoms of varicose veins: fatigue, feeling of heaviness, aching pain, burning and tingling, throbbing, itching, cramps and restlessness. Also, one of the symptoms may be the appearance of swelling of the legs. As a result of a pronounced expansion of varicose veins, a violation of the blood supply to the tissues of the lower extremities can develop, skin defects occur in the form of darkening or redness, inflammation. In an extremely neglected case of varicose veins, trophic ulcers develop.
Diagnosis of varicose veins
To establish a diagnosis, the doctor, first of all, examines the patient, paying special attention to the appearance and swelling of the lower extremities. You may also be asked a series of questions about how you feel to clarify the nature of the pain. Also an important step is to perform a series of tests to assess the functional state of the superficial and deep veins. And, finally, an ultrasound Doppler study of the main veins of the lower extremities. The ultrasound method allows the doctor to see the structure and evaluate the function of the veins of the lower extremities, as well as to identify venous blood clots.
When the first symptoms of the disease appear, you should consult a doctor dealing with diseases of the vessels and, in particular, veins (general surgeon, vascular surgeon and phlebologist), and if the skin is damaged, you should also visit a dermatologist. Only after visiting specialist doctors, on their recommendation, you can contact a cosmetology clinic.
Prevention of varicose veins
Currently, there is no method that would completely prevent the development of varicose veins. Thanks to prevention, it is possible to improve muscle tone, which helps to improve microcirculation in tissues, as well as improve the condition and function of the veins of the lower extremities, and reduce the risk of complications. The traditional and most widely used methods of prevention are as follows:
- Exercise stress. Move more. Your legs must be constantly in motion. During the walk, more favorable conditions are created for blood circulation in the lower extremities. Check with your doctor. It will help you choose the most optimal type and level of physical activity.
- Control your weight. Being overweight increases the load on the circulatory system and, in particular, on the veins. Also, with excessive salt intake, edema increases most pronouncedly as a result of fluid retention in the body.
- Pay attention to what you are wearing. Avoid high heels. Your shoes should always be comfortable. When wearing shoes with low heels, your lower extremity muscles work much better, which helps to improve venous outflow. Also, do not wear uncomfortable and tight trousers and skirts.
- Raise your legs. When lifting the legs, the venous outflow of blood from the lower extremities improves. Try to take a few breaks during the day and lift your legs up. For example, lie on your back and put your feet on a pillow.
- Avoid prolonged periods of standing or walking. To improve blood circulation, try to change the position of your body as often as possible. Try to get up and walk around every 30 minutes.
- Don't cross your legs. Sitting cross-legged creates unfavorable conditions for blood flow in both lower extremities.
For the prevention of varicose veins, a good remedy is to wear stockings, golf and a sock with a compression effect. It can also be a good addition to the main (drug or surgical treatment). Currently, pharmacies offer a wide range of compression underwear for your choice.
Treatment of varicose veins
There are several generally accepted treatments for varicose veins in the legs:
- conservative (drug and compression therapy).
- surgical.
Conservative treatment
Doctors consider elastic compression to be the most effective conservative treatment and prevention of varicose veins - the use of special compression stockings (stockings, golf, tights). When wearing this jersey, uniform pressure is provided on the lower limbs, which contributes to normal blood circulation and improvement of its outflow, while forming, as it were, an external frame that supports weakened vascular walls. As a result, the load on the veins decreases, the outflow of venous blood improves and the rate of further progression of the disease decreases, the risk of developing thrombosis decreases.
Modern compression hosiery is divided into two types: therapeutic and prophylactic. Each medical product is marked in mm Hg, according to which it is divided into classes from I to IV. At different stages of the disease, compression of a certain strength is used and it is necessary to consult a doctor, since only a doctor can prescribe and choose the right compression stockings, taking into account the nature of the pathology and according to certain individual measurements.
With a sedentary lifestyle, as well as with prolonged physical exertion, during pregnancy or with a hereditary predisposition, it is recommended to wear preventive compression stockings and tights. If even slight signs of varicose veins appear, you should immediately contact a specialized clinic.
Drug therapy can reduce the clinical manifestations of the disease - pain, swelling, discomfort, convulsions, and so on, but cannot completely stop the progression of the disease and is used today only as part of complex therapy during the main surgical treatment. Unfortunately, most of the drugs currently offered on the pharmaceutical market for the treatment of varicose veins have a rather low efficiency, despite the theoretically justified expediency of use. One of the reasons for this is the low absorption by the body of the medicinal substances underlying these drugs. It is possible that in this situation an increase in the dose of the drug taken would help, but this is associated with an increased risk of complications and side effects. Another reason for the low effectiveness of these drugs is that their spectrum of action is relatively narrow and is directed at one link involved in the development and progression of the disease. And to achieve the optimal effect, a complex effect on the disease and the use of several drugs is necessary. An ideal drug for the treatment of venous insufficiency and varicose veins should affect as many pathogenic links of chronic venous insufficiency as possible, while having a minimum number of side effects and being well absorbed by the body.
Surgery
To date, surgical treatment of varicose veins in the legs does not require a long stay in the hospital. Thanks to the use of modern invasive methods of treatment, the removal of varicose veins can be carried out not only under anesthesia with the patient's consciousness completely turned off, but also under local anesthesia, when the patient is in clear consciousness, only the pain sensitivity of the lower extremities is turned off. Varicose veins within 3 months after delivery disappear on their own without any treatment.
There are the following surgical methods of treatment:
- Sclerotherapy.During this procedure, a solution is injected, under the influence of which a scar is formed at the site of the damaged vein. This method is applicable only for small and medium sized varicose veins. Occasionally, not one, but several injections of a sclerosing solution may be required for the complete disappearance of the vein. Sclerotherapy is quite effective if carried out correctly, is less traumatic, leads to a good therapeutic and cosmetic effect, and a significant advantage is that sclerotherapy is performed under local anesthesia (i. e. without anesthesia), directly in the doctor's office.
- laser surgery.To remove varicose veins of any diameter and, in particular, the venous mesh, laser radiation can be used. The essence of the method is to irradiate the inner surface of the vein with a laser beam. Through a small puncture of the skin and the wall of the vein, a special device is inserted - a light guide, through which a laser beam is passed under ultrasound control. The inner surface of the vein is irradiated with a laser, then it is glued together. When applying this method, the doctor aims a laser beam at the vein that should be removed, a slow discoloration and complete disappearance of the vein occurs. An important advantage of this method is that neither soft tissue nor skin incision is made. Using the laser method, it is possible to eliminate the affected veins and heal trophic ulcers of the lower leg.
- Removal of a varicose vein surgically.During surgical removal, a number of small incisions are made in the skin and soft tissues, through which the damaged vein is removed and the insufficient perforating veins of the leg are ligated. When using this technique, anesthesia is a necessary condition. This method is used to remove large diameter varicose veins.
- Outpatient phlebectomy (removal of varicose veins).This method is applicable to the removal of small diameter veins. With this method, the vein is removed through several small incisions in the skin under local anesthesia. The scars formed after removal are small and almost invisible.
- Endoscopic removal of varicose veins.This method is especially well suited for the formation of skin defects in the form of ulcers. During this method, a special video microcamera is inserted into the vessel, which allows you to see the vessel from the inside and observe its entire removal procedure. The vein is then removed under supervision through this chamber.
Thanks to the use of modern methods of treatment, it is possible to achieve a complete cure and a good cosmetic effect. But it should be remembered that varicose veins can reappear.
Complications of varicose veins
Occasionally, on the skin around a varicose vein, as a result of a violation of blood microcirculation, changes can occur from severe darkening to ulcerative defects of the skin. If these changes occur, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Another more formidable complication of varicose veins is the development of blood clots in the deep and superficial veins. This complication is called thrombophlebitis. When it occurs, acute unbearable pain, swelling and redness appear. In this situation, you should also immediately consult a doctor.
Causes of varicose veins
The true nature of varicose veins is not clear enough. According to most scientists, varicose veins are hereditary, genetically determined. The main reason for it is the weakness of the vein wall and dysfunction of the venous valves. The venous valves originate from the wall of the veins and normally have 2 leaflets oriented towards the heart. With normal closure of the valves, blood from the overlying section of the vein cannot penetrate into the underlying section. In case of dysfunction of the valves and incomplete closure of the valves, the blood moves up and down, resulting in venous stasis and expansion of the veins located below the valve with impaired function. Initially, a varicose vein appears in the place where there is a valve with impaired function, and blood is discharged from the deep veins to the external ones, the overflowing vein stretches, expands, which leads to stretching and dysfunction of the underlying valve, and so on. Gradually, disturbances in the venous outflow of blood from the lower limb to the heart develop, as a result of which blood microcirculation in the tissues of the lower limbs is disturbed, which is manifested by edema, increased pigmentation, thrombophlebitis and trophic ulcers.
Factors in the development of varicose veins
Factors contributing to varicose veins can be:
- Genetic predisposition - a thin and weak wall of superficial veins.
- Increased pressure on the veins: sedentary work, prolonged standing, wearing uncomfortable shoes with high heels, heavy lifting, lack of movement of the calf muscles. Also a triggering factor for the development of varicose veins is pregnancy and childbirth. With a sharp physical overstrain, there is a strong increase in hydrostatic pressure in the veins of the lower extremities, which triggers the process of their varicose expansion.
Other risk factors for developing varicose veins include:
- Age. With age, the wall of the veins, as well as the valves, become thinner, which leads to a regular violation of their function.
- Floor. Women are more likely to suffer from varicose veins. It is possible that this is due to a number of hormonal reactions. Female sex hormones affect the process of relaxation of the venous wall. Pronounced hormonal changes in the female body occur during pregnancy and childbirth, during the menstrual cycle and during menopause, which cannot but affect the function of the venous system. It is also impossible to exclude the influence of taking hormonal contraceptives on the process of varicose veins.
- Obesity. With overweight and obesity, the load on the veins of the lower extremities increases.
- Pregnancy and childbirth. In pregnant women, the volume load in the body increases, but at the same time, the rate of blood outflow from the lower extremities to the pelvic cavity into the system of the inferior vena cava and to the heart decreases. Thus, favorable conditions are created for the development of varicose veins. Changes in the circulatory system in a woman's body ensure the development of the fetus, but at the same time they cause the development of varicose veins. With the course of pregnancy or during childbirth, the progression of varicose veins is possible not only in the lower extremities, but also in the hemorrhoidal veins around the anus.