In our modern world, this problem is very acute and widespread in both men and women. We will try to find out the reasons, predisposing factors, and also talk about the methods of treatment and medicines used for varicose veins.
Varicose veins are a disease of the veins characterized by their enlargement, change in shape and decrease in their elasticity. Most often, the superficial veins of the lower extremities, the venous plexus of the rectum (hemorrhoids), the veins of the collar system and the spermatic cord are affected.
Predisposing factors
Conditions that contribute to the obstruction of the outflow of blood through the venous system, namely:
- systematic long-term stay on feet associated with professional activities (waiters, pharmacists, hairdressers, salespeople, etc. );
- compression of the pelvic veins by the pregnant uterus;
- congestion in the veins of the pelvis, for example, with chronic constipation, sedentary work;
- congenital weakness of the venous wall and insufficiency of the venous valves;
- surgical intervention (arteriovenous shunting);
- hormonal imbalance (menopause, estrogen intake);
- overweight.
It is important that the true causes of varicose veins are not known. This disease is progressive in nature, and refers to irreversible changes in the venous vessels.
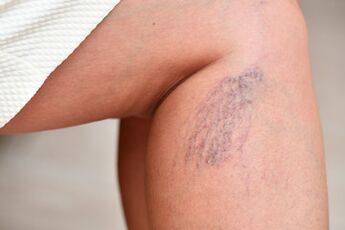
If we talk about varicose veins of the lower extremities, then it is also a cosmetic problem for women. The dilated veins show through or swell under the skin in the form of twisted cords or knots (varicose veins). The skin on them is thinned and easily damaged, the cause is a violation of its nutrition. First, dark brown or brown spots appear on the skin, then the veins twist and lift the skin. Over time, if the skin nutrition is disturbed, trophic ulcers can form. Varicose veins are almost always accompanied by swelling of the extremities, which appears towards the end of the day. This condition leads to rapid fatigability of the legs when walking, a feeling of heaviness and pain in the legs, increasing in the evening. In the absence of appropriate treatment, the disease progresses and the swelling of the extremities increases. Due to the slowing down of blood flow, inflammatory processes can occur in the dilated veins, leading to their blockage.
Thus, the stages of varicose veins:
- 1 "heavy" legs syndrome;
- 2 persistent edema develops, accompanied by a violation of skin pigmentation and congestive dermatitis;
- 3 trophic ulcers appear.
Symptoms of varicose veins of the lower extremities
- rapid fatigue of the legs when walking;
- convulsions at night;
- feeling of heaviness in the legs;
- pain in the legs, worse in the evening;
- tension in the legs;
- heart palpitations and shortness of breath. These symptoms occur when the load on the heart muscle increases due to the deposition of blood in the venous bed.
Consider when varicose veins are localized in other organs:
Varicose veins of the esophagus
Varicose veins of the esophagus are characterized by tortuosity and saccular growths of blood vessels. The cause of the disease is portal hypertension.
Manifestations:
- inflammation of the esophagus;
- burning, belching;
- anemia;
- difficulty swallowing.
The development of such complications as significant bleeding from the veins is possible. The patient has vomiting with blood, hypotension, tachycardia, impaired consciousness.
Varicose veins of the uterus
The reasons:
- increased physical activity;
- chronic constipation;
- pregnancy;
- taking hormonal contraceptives;
- developmental anomalies;
- abortion.
Symptoms are painful sensations in the lower abdomen, menstrual irregularities. A dangerous complication is infertility.
Varicose veins of the labia
It occurs most often in the second month of pregnancy. Pelvic vein thrombosis or congenital angiodysplasia is a predisposing factor.
Manifestations:
- enlarged veins of the vulva;
- scratching and swelling of the skin;
- bursting pain in the perineum.
Development of acute thrombophlebitis, rupture of the damaged vessel is possible.
Varicose veins of the small pelvis
In the initial stage, it is manifested by pulling pains in the lower abdomen. There are several options for the course of this form of the disease:
- varicose veins of the perineum and vulva;
- pelvic venous congestion: pain during intercourse, dysmenorrhea, urinary disorders.
Clinical manifestations of pathology are observed in 30% of women during pregnancy. This disease is observed exclusively in women.
Varicose expansion of the spermatic cord (varicocele)
Due to the varicose expansion of the spermatic cord, venous outflow from the testicles is disturbed. Patients note nagging pain in the scrotum, erectile dysfunction. On examination, dilated superficial veins and scrotal asymmetry are visible in the testicular area.
The reasons:
- increased physical activity;
- congenital connective tissue failure;
- tumors in the retroperitoneal space or pelvis.
Possible complications in the progression of the disease are spermatogenesis leading to infertility.
Varicose dermatitis
This disease is manifested by thinning and itching of the skin over the affected veins. In places of inflammation, spots of dark or light color and peeling appear. The main localization of venous dermatitis is the lower leg and the ankle joint. The danger is that patients scratch the itchy areas and the pathological process goes to healthy tissues. If you do not resort to treatment, then the inflammation turns into varicose eczema.
Varicose eczema
The inflammation is persistent with periods of remission and relapse. Skin lesions are difficult to treat even after venectomy. Due to the violation of skin microcirculation, the liquid part of the blood passes through the walls of the affected vessels. In the area above the varicose vein, swelling and weeping areas appear.
Vesicles with serous or serous-purulent contents appear on the legs. When scratching, an infection develops in the wounds. Merging, small bubbles form papules. After opening the vesicle, crusts appear. The healing site is thinned and covered with scales. During the period of exacerbation, vesicles reappear. The progression of pathology leads to the formation of trophic ulcers.
Vascular spiders
Vascular asterisks - telangiectasias. They are characterized by the defeat and expansion of small subcutaneous vessels. They look like a purple or red vascular network on the skin. In general, it is not a separate disease, but rather acts as a cosmetic defect.
The reasons:
- venous insufficiency;
- connective tissue diseases;
- pathology of the hepatobiliary system;
- the use of hormonal drugs;
- endocrine system diseases.
Vascular meshcan be localized on the legs, face or buttocks. On the face, the manifestations of the vascular network are called rosacea.
The reasons:
- violations of the rheological properties of blood;
- arterial hypertension;
- diseases of the digestive system;
- the effect of low temperatures on the skin in a special way;
- when drinking alcohol.
A common cause of rosacea in women is hormonal changes and is eliminated by laser coagulation.
With varicose veins, preventive measures are of great importance:
- use of comfortable shoes and non-constricting underwear;
- if there is a predisposing factor or disease at the initial stage, then it is necessary to limit or exclude static loads and prolonged stay on the legs;
- moderate physical activity;
- taking vitamins: C, E, PP;
- balanced diet.
Of course, in the present modern world, follow the recommendations on limiting or eliminating static loads and staying on your feet for a long time, therefore, it is necessary to resort to short gymnastics during the day, as well as to use massage services. It is also mandatory to wear elastic bandages and compression underwear.
Diagnostics
Comprehensive diagnostics is carried out using laboratory methods for examining blood and urine (detection of reflux in the saphenous veins, functional tests) and ultrasound examinations: ultrasound duplex or triplex scanning; radiopaque phlebography; magnetic resonance phlebography; multispiral computed angiography with contrast.
Treatment
After receiving the diagnostic results, the phlebologist (angiosurgeon) decides on the use of treatment methods - surgery or conservative therapy.
In case of damage to the vessels of the lower extremities, apply:
- surgical intervention, for example, phleboectomy - removal of a specific vein;
- sclerotherapy;
- conservative treatment.
Systemic drug therapy
- Antibiotics(prescribed in the presence of inflammatory processes and trophic ulcers;
- Antiseptics;
- Phleboprotectors;
- Tissue regeneration stimulants;
- Anticoagulants;
- Topical steroids (prescribed for trophic ulcers);
- Outwardly - heparin-containing drugs.
In this article, we will dwell in detail on phleboprotectors and external agents used for varicose veins.
Phleboprotectors (Phlebotonics) are a group of medicines used for venous insufficiency. They increase blood circulation, thereby normalizing vascular patency, relieve puffiness and eliminate the feeling of heaviness. It is important to use them at the initial stages of the disease or for the prevention of exacerbations; with progressive forms, several courses of treatment are prescribed by different groups.
Review of medicines used for varicose veins.
Natural remedy based on the extract of red grape leaves.Able to protect the walls of blood vessels and capillaries, improving their elasticity, normalizes vascular permeability.
The tool is distinguished by improved protection of the walls of blood vessels and capillaries. The drug removes puffiness and prevents its recurrence, as it blocks the permeability of water, proteins and plasma through the walls of blood vessels, achieving restoration of their natural density.
Shown at:
- prevention and symptomatic treatment of chronic venous insufficiency;
- swelling of the lower extremities;
- with sensations of heaviness and fatigue in the lower extremities.
Contraindicated:
- people who are allergic to one of the components in the composition.
Apply 1 capsule upon awakening. The doctor may increase the dosage to 2 capsules.
Diosmin
The drug is available in pill form and is sold without a doctor's prescription. It belongs to venotonic and angioprotective agents. Diosmin increases venous tone, reduces venous congestion, improves capillary permeability and microcirculation. Has a decongestant effect.
Shown at:
- varicose veins in the limbs and pelvis;
- complex therapy of hemorrhoids;
- signs of venous insufficiency, disorders of lymph flow.
Contraindicated:
- with increased sensitivity to components;
- children and adolescents up to 18 years old.
Of the side effects, mild digestive upset and headache are possible. Apply 1 tablet in the morning. The course of treatment can be quite long, but usually no more than 2 months.
Troxerutinrelieves puffiness, normalizes microcirculation and strengthens the walls of blood vessels. It has anti-inflammatory, antioxidant effects.
Shown at:
- chronic venous insufficiency, at any stage of the disease;
- phlebeurysm;
- superficial thrombophlebitis;
- periphlebitis, phlebothrombosis;
- varicose dermatitis;
- post-thrombotic syndrome;
- hemorrhoids;
- post-traumatic edema and hematomas;
- hemorrhagic diathesis with increased capillary permeability;
- as a prophylactic agent after vein surgery.
Troxerutin is used in combination with ascorbic acid to enhance its effects after vein surgery.
Contraindicated:
- with hypersensitivity;
- peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum;
- chronic gastritis (in the exacerbation phase).
Not suitable for persons under the age of majority, pregnant in the first trimester, lactating. The drug Troxerutin should not be used if there are problems with the gastrointestinal tract. In the active stage of the fight against the disease, 1 capsule is prescribed along with meals three times a day. To maintain the effectiveness of treatment, the agent is applied twice a day.
Rutosidehas anti-inflammatory effects and fights swelling and heaviness in the legs. The peculiarity of the drug is that it works with blood cells, promoting patency. Thus, the medicine for varicose veins contributes to the fight against microthrombosis of the veins.
Shown at:
- chronic venous insufficiency;
- postphlebitic syndrome;
- trophic disorders with varicose veins, trophic ulcers;
- hemorrhoids (pain, exudation, itching and bleeding);
- venous insufficiency and hemorrhoids during pregnancy, starting from the second trimester.
Contraindicated:
- during pregnancy, for a period of 1 to 3 months.
The capsules are used 2-3 times a day, one at a time.
Tribenosideavailable in the form of pills and capsules. It has a decongestant, anti-inflammatory effect, improves vascular permeability.
Shown at:
- varicose veins of the lower extremities, including in the second and subsequent stages;
- CVI symptoms, namely: lymphostasis, blood congestion, a feeling of pain, heaviness, distention in the calf region of the legs, especially in the evening;
- phlebitis, periphlebitis, postoperative period;
- trophic ulcers;
- hemorrhoids in chronic and acute phases.
Contraindicated:
- pregnant women at 4-12 months and lactating women.
Capsules are taken 2 times a day at regular intervals.
Diosmin with hesperidin,the drug is available in the form of film-coated tablets, available without a doctor's prescription. The main active ingredients are diosmin with hesperidin. They belong to the group of venotonic substances and angioprotective drugs. They help to restore the tone of the venous walls and improve blood flow in the veins, and normalize the functioning of the valves.
Indications for use:
- hemorrhoids;
- varicose veins of the extremities and small pelvis;
- chronic venous insufficiency, including trophic ulcers.
The drug is contraindicated in case of allergic reactions to the components and the period of breastfeeding. Among the side effects, only mild dyspeptic symptoms, a skin rash can be distinguished. The drug is indicated for complex and course admission.
External remedies for the complex treatment of varicose veins
Ointments and gels are used as external agents. First of all, it is necessary to provide anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects; for these purposes, anti-inflammatory drugs of non-steroidal origin are used, as well as steroid drugs of general action.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs):
- Ketorolac;
- Ketoprofen;
- Ibuprofen;
- Nimesulide gel;
- Diclofenac;
All of them have a powerful anti-inflammatory effect, eliminate pain, discomfort, and severity. are used 1-3 times a day, depending on the stage of the disease, with circular massage actions. Contraindicated in the presence of trophic ulcers and open wounds.
Steroids are used in special cases. If NSAIDs are ineffective.
Prednisolone and its analogues.Inflammation and pain are relieved, and local tissue nutrition is improved. It is not used in large quantities, due to the possibility of provoking side effects of a generalized nature.
Removal of puffiness:
Medicines based on corticosteroids are used. Restoration of normal blood flow in the legs with varicose veins, by stimulating the contraction of the vascular walls:
- Troxerutin;
- Diosmin;
- Rutoside.
Narrowly anesthetic external medicines are rarely used, due to their limited action, they do not eliminate the cause, but work with symptoms:
- Diclofenac;
- Ketoprofen.
Heparin-containing drugs, in addition to heparin, contain corticosteroids.
Complex ointments used for varicose veins of the legs
These drugs have a systemic effect:
- Heparin sodium (used to relieve swelling, pain, improve local blood flow, prevent the formation of blood clots. It has a quick therapeutic effect: it is achieved on the second or third day of use).
- Troxerutin. It relieves pain, swelling, inflammation, normalizes the condition of the veins, provides adequate venous-lymphatic outflow, and prevents the formation of blood clots.
- Escin. It is prescribed in the early stages of varicose veins of the legs, in the later stages it is almost ineffective. It is of vegetable origin.
Basic principles of therapy with external drugs:
- do not self-medicate, but resort to the help of a phlebologist;
- strictly follow the instructions for use;
- analyze the result of the effectiveness of treatment after 10 days from the date of treatment.
However, even with the combined use of tablets and ointments, gels for external use, you should not count on a quick result, it all depends on the progression of the disease, its stage and the presence of concomitant diseases.
In conclusion, I would like to note that drugs for varicose veins at various localizations are not able to completely stop the disease and prevent complications. In the early stages of the disease, venotonic and angioprotective drugs help to normalize blood flow inside the lower extremities, eliminating symptoms such as swelling, leg fatigue and spider veins, protruding convoluted superficial veins. All of these medicines are only part of the treatment that is directly related to lifestyle and nutrition. In progressive stages, microsurgical and minimally invasive interventions are indicated while taking drugs that improve the outcome of therapy.